The Paleo Diet

What is the Paleo Diet?
Obesity, heart disease, and diabetes are just a few of the health conditions caused by our sedentary lifestyles and modern unhealthy diets with huge amounts of sugar and fat. The Paleolithic diet, or the caveman diet, is the proposed solution to this issue. Cut modern foods from your regular diet and return to the way our early hunter-gatherer ancestors ate. To be healthy on the paleo diet, people following the diet eat only foods that were available during the Paleolithic period when humans hunted and gathered all their food and also adopt a more active lifestyle by exercising regularly.
How does it work?
The Paleo diet is said to promote a more natural way of eating with low levels of sugar & salt plus the elimination of processed, refined foods. The idea is that this is more in tune with how our bodies have evolved and how over the centuries we would have fuelled ourselves. As a consequence, the plan typically omits dairy foods, cereal grains, starchy vegetables as well as sugar in favour of lean animal foods, non-starchy fruit and vegetables and honey.
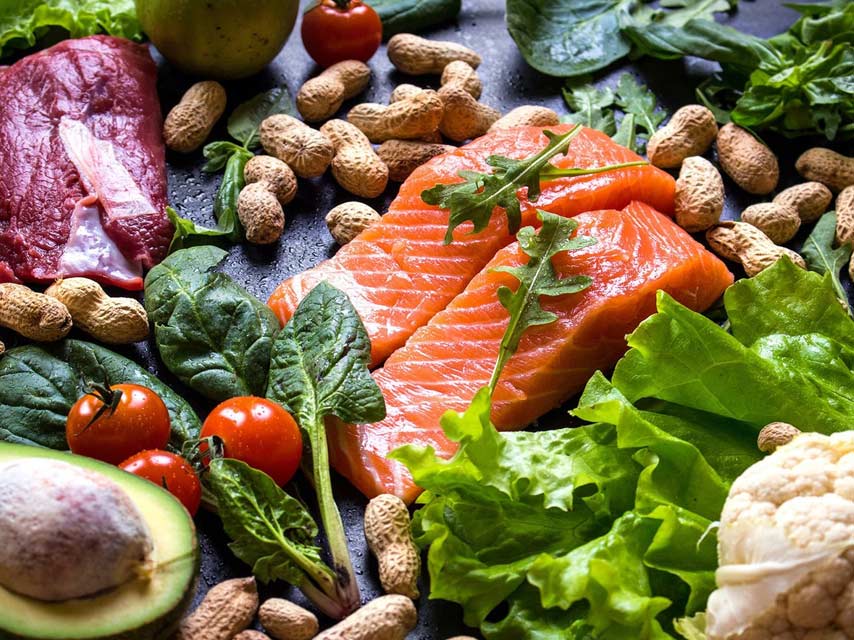

Benefits derived from the Paleo Diet
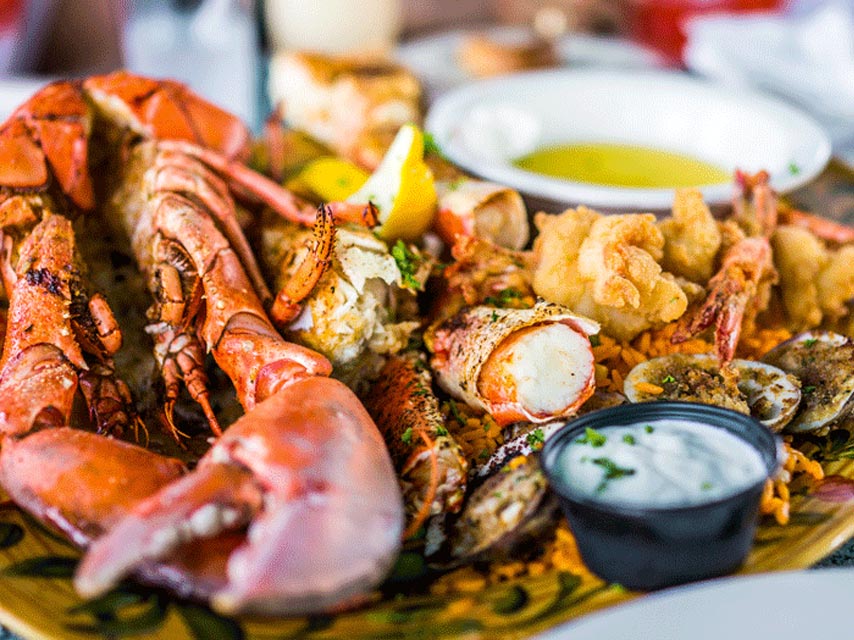
The diet is not low fat but instead promotes the inclusion of natural fats from pasture-fed livestock, fish and seafood as well as seeds and their oils. The elimination of such a wide range of foods like grains, dairy, processed foods and sugar means the diet is more than likely to lead to some weight loss. Healthy fats are encouraged such as the unsaturated varieties and specifically oils like olive, flax, walnut and avocado. There are anti-inflammatory benefits from the plant nutrients in fruits, vegetables, oils, nuts, and seeds. Too much inflammation in the body can increase the risk of health problems, including type 2 diabetes, but eating low-carb, low GI foods – particularly omega-3 fatty acids - can protect against excess inflammation. Several studies have reported the paleo diet can have benefits for heart health. This is particularly useful for people with diabetes as heart disease is one of the most common diabetes-related complications. Other benefits may also include improved total cholesterol:
The Paleo Diet Plan
What to eat:- Grass-fed meat
- Fish and seafood
- Fresh fruits and veggies
- Nuts and seeds
- Healthy oils - olive, walnut, flaxseed, macadamia, avocado, coconut
- Grains (wheat, rye, barley, corn, rice, etc.)
- Beans & Legumes (soy, lentils, black beans, garbanzo beans, peanuts, red or white beans, etc.)
- Dairy (milk, cheese, yogurt, ice cream, etc.)
- Refined sugar & artificial sweeteners

Healthy guidelines
Limiting Protein Intake
The key is in limiting cuts high in saturated fats- stick mainly with organic poultry and fish. If you choose red meat, keep it lean and preferably grass-fed. Include it in no more than two or three meals a week. Too much meat also potentially increases chronic health risks such as heart disease.Quality of Carbohydrates
Consuming simple carbohydrates give your body a high elevation in blood sugar that results in an equally low swing in the opposite direction, meaning after insulin kicks in and lowers your blood sugar, your body craves food to push it back up. You feel hungry quickly. The long-term result is a complete loss of control in the way you handle your food intake. However, you need to be careful about the quantity of carbs you’re consuming. Too many carbs and your body won’t burn fat. Too little carbs, and your body burns through your muscle tissue. To strike a healthy balance, it’s important to choose complex carbohydrates as much as possible, such as vegetables and fruits.Planning Ahead
Planning your meals for the week include more than just dinners - don't forget about breakfast, lunch, and snacks. It is also important to consider your options when dining out and how strict are you about the diet.You may also like
Comments


 French
French


